资源说明:ThreeAudio helps you create music visualizations in Three.js or tQuery.
ThreeAudio.js
==========
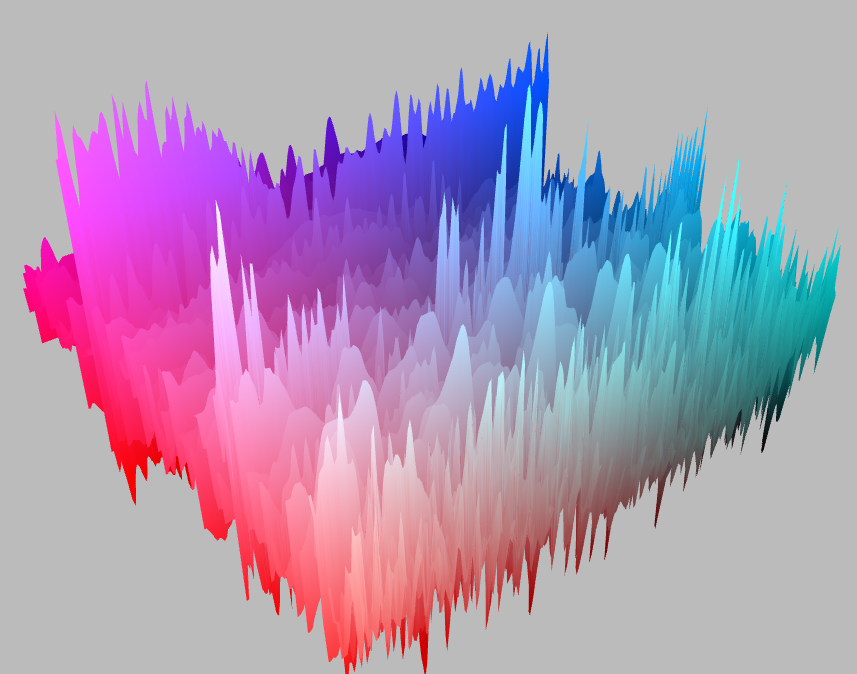
ThreeAudio helps you create music visualizations in Three.js, by exposing audio data in GLSL shaders.
It can be used directly with Three.js or as a tQuery plug-in.
* * *
ThreeAudio will read from an audio source and provide frequency/time data in the form of textures, as well as derived values for volume, bass, mid range and treble. ThreeAudio also includes a real-time beat detector based on autocorrelation.
Use the included ThreeAudio.Material class to create ShaderMaterials that can read from the audio data.
Includes: microevent.js (Jerome Etienne), dsp.js (Corban Brook)
*NOTE: ThreeAudio is still somewhat experimental and only Webkit Audio APIs are supported for now. Patches are welcome.*
Demo (Chrome only!): [http://acko.net/files/three-audio/](http://acko.net/files/three-audio/)
Builds:
* ThreeAudio: microevent + core
* ThreeAudio-tquery: microevent + core + tQuery plug-in
* ThreeAudio.glsl.html: required GLSL shaders
Basic Usage
-----
1) Stand-alone
Create an audio source, load a file and request playback when ready.
```javascript
var audioSource = (new ThreeAudio.Source()).load('/audio/file.mp3').play();
```
Create textures to hold the audio data, passing in the Three.js renderer and the audio source.
```javascript
var audioTextures = new ThreeAudio.Textures(renderer, audioSource);
```
Create a material that uses the audio data, passing in the audio textures, a vertex/fragment shader program, as well as any other textures, uniforms and attributes you wish to use (as objects with key/value pairs). Specify a literal vertex/fragment program, or the ID of a script tag that contains the source code for the program.
```javascript
var audioMaterial = new ThreeAudio.Material(audioTextures, vertexShader, fragmentShader);
// Or
var audioMaterial = new ThreeAudio.Material(audioTextures, vertexShader, fragmentShader, textures, uniforms, attributes);
```
Apply the material to a mesh and insert it into your scene. Use `GridGeometry` to get a plane with UV coordinates that are perfectly aligned with data samples.
```javascript
// Sample entire data set
var geometry = new ThreeAudio.GridGeometry(audioTextures, 100, 100);
// OR: 16 frequency/time samples and 5 history samples
var geometry = new ThreeAudio.GridGeometry(audioTextures, 100, 100, 16, 5);
// Mesh
var audioMesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, audioMaterial);
scene.add(audioMesh);
```
Update the audio textures every frame before render.
```javascript
audioTextures.update()
```
2) tQuery
Create an audio source and start playing.
```javascript
var audio = world.audio().load('/audio/file.mp3').play();
```
Create audio textures, make a material out of them with given shaders, and bind it to a mesh. Use .grid() on the material to get a planar grid ready for rendering.
```javascript
var mesh = audio.textures().material(vertexShader, fragmentShader).grid().addTo(world);
```
Note: the textures are automatically updated on render. The chained calls above give you access to the intermediate ThreeAudio objects in between.
Shaders
-------
See `shaders/shaders.glsl.html` for an example shader that generates a 3d spectrum voiceprint.
* * *
Steven Wittens - http://acko.net/
本源码包内暂不包含可直接显示的源代码文件,请下载源码包。
 English
English
